⟰ Department of Computer Science

MAChine Communication with Humans and Inference in NAtural environments (MACCHINA)
Project financed by Internal Funds KU Leuven (C14/18/065)
2018-2022
Context
The MACCHINA project advocates a new paradigm for multimodal problems that is based on learning continuous embeddings that are spatially aware. The goal of MACCHINA is to create a system that conducts a natural language dialog with a user about the joint visual context. The way MACCHINA realizes this is divided in four different parts that will all work together.
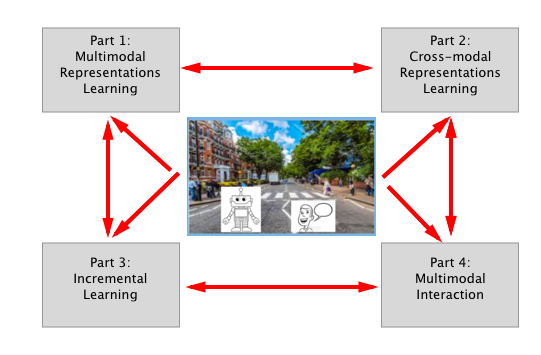
The four different parts in MACCHINA.
The different parts
Part 1: Multimodal Representations Learning
- Current baselines fail to associate entities in text with the corresponding image pixels and often align to irrelevant image regions.
- The goal is to impose structure on the alignment or attention models leveraging the grammatical structure of language and the geometric structure of the images so as to make the models more robust for unseen compositions.
Part 2: Cross-modal representations learning
- Another way of building representations jointly informed by images and language is by considering the process as a translation process. What is meant by this is that when we are given an image, the output will be a language description. Or if we've given a language description we output an image.
- By repeating this translation process a multimodal dialog system can be created.
Part 3: Incremental learning
- For a dialog system it is interesting to gradually pick up new concepts.
- By exploiting the learned multimodal embeddings new concepts can be learned given a much lower number of occurrences.
Part 4: Multimodal interaction
- During dialogs with humans it is important that objects and actions in both the language and the visual context correctly co-refer. The problem is that humans often use synonyms, adjective and adverbial expressions to refer to objects and actions.
- What is said and what is seen needs to be translated to geometric positions in a real physical world so that consequent actions by the machine can be correctly performed.
Applications
 Image source
Self driving cars
Image source
Self driving cars
By integrating MACCHINA in self- driving cars passengers are be able to have a dialog with the car about its next action (ex: Where to park the car? In the sun or in the shade?)
 Image source
Surgical robots
Image source
Surgical robots
Integrating MACCHINA in surgical robots could help surgeons during operations by allowing them to give verbal instructions. The robot then might be able to recognize but also predict certain medical events.
Related
- Amazon partners with Lamborghini to implement Alexa in their supercars. [website]